카테고리 없음
블록, hash, merkleroot(tree)
kim help
2022. 6. 8. 13:47
블록 개념
- 블록헤더 : 비전,이전 블록의 해시, 머클루트, 타임스탬프,난이도 목표, 넌스
- 거래 카운터 : 거래의 개수
- 거래 : 블록에 기록된 거래내역
merkleRoot
이진트리 > 거래를 두 개씩 묶는다
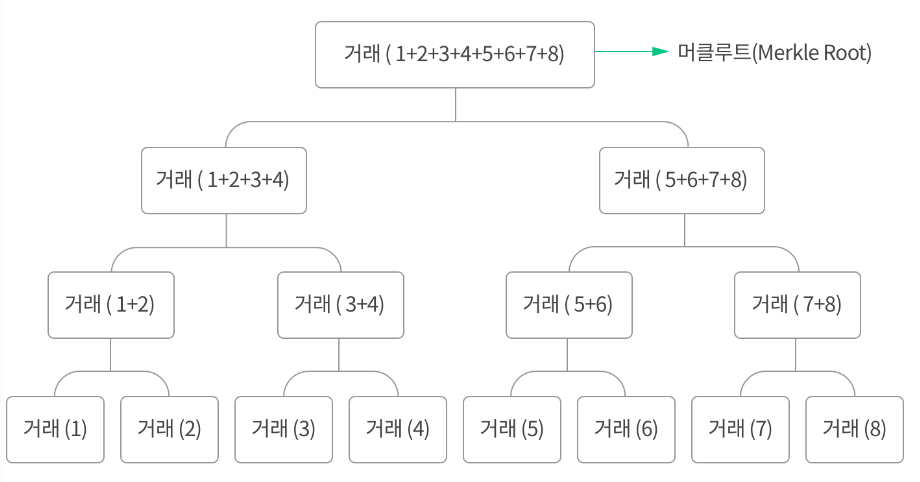
장점 : 거래량이 기하급수적으로 늘어나도 특정 거래를 찾는 경로는 단순하다.
거래 위변조도 쉽고 빠르게 알 수 있게 되고 이를 방지 가능
1. npm install crypto-js
디렉토리 구조
1) 해쉬
SHA-256 해시를 사용
- 고정된 길이의 출력값 : 64자리
- 눈사태 효과 : 데이터의 입력값이 조금이라도 차이가 있다면 완전히 다른 해시 출력밧을 도출
- 충돌 회피성 : 해시가 서로 다른 두 개의 입력값에 대해 동일한 출력값을 도출하는 상황이 적다
- 단방향성 : result로 보여지는 해쉬 값은 원래 값으로 돌아갈 수 없다.
- 임의성 : 해시는 출력값을 도출하는 공식을 찾을 수 없게 일정한 포맷을 기준으로 임의로 출력값을 변환
const SHA256 = require('crypto-js/sha256')
// 단방향
const a = 'hello hash'
// 암호화
console.log('result :',SHA256(a).toString());
// 암호화된 값의 길이
console.log('length :',SHA256(a).toString().length);
값
result : e08e1d7bd3fec53b7360de39482ac30d8d1b7bedead27e013810e29095fee6fb
length : 64
2. npm install merkle
2) merkleRoot
2개씩 짝지어서 더해서 해쉬값을 만든다. 1+2 , 3+4
1 1+2=64 , 2 3+4=64
1+2 =64 > merkleRoot
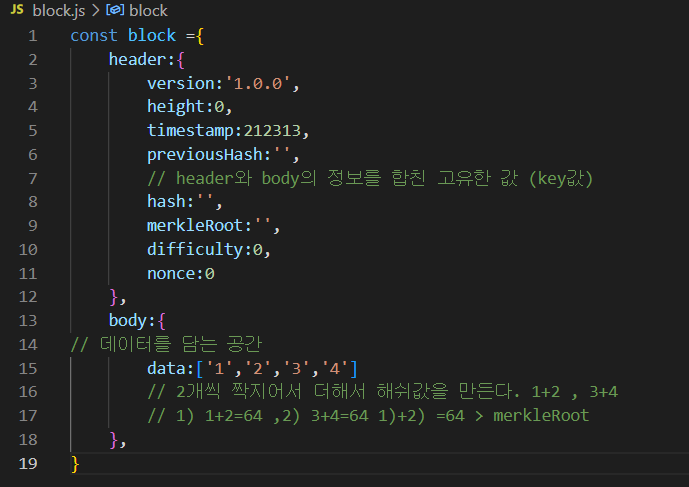
바디 값들을 더한다.
body:{
// 데이터를 담는 공간
data:['1','2','3','4']
},
전체 코드
// const block ={
// header:{
// version:'1.0.0',
// height:0,
// timestamp:212313,
// previousHash:'',
// // header와 body의 정보를 합친 고유한 값 (key값)
// hash:'',
// merkleRoot:'',
// difficulty:0,
// nonce:0
// },
// body:{
// // 데이터를 담는 공간
// data:['1','2','3','4']
// // 2개씩 짝지어서 더해서 해쉬값을 만든다. 1+2 , 3+4
// // 1) 1+2=64 ,2) 3+4=64 1)+2) =64 > merkleRoot
// },
// }
const merkle = require('merkle')
const { SHA256 } = require("crypto-js")
// 객체를 쉽게 만들기 위해 function or class 를 쓴다.
class BlockHeader{
constructor(_height,_previousHash =''){
this.version = this.getVersion()//X
this.height = _height//O
this.timestamp = this.getTimestamp()//X
this.previousHash = _previousHash=='' ? "0".repeat(64) : _previousHash
}
getVersion(){
return '1.0.0'
}
getTimestamp(){
return new Date().getTime()
}
}
class Block{
constructor(_header,_data){
const merkleroot = Block.getMerkleRoot(_data)
this.version= _header.version,
this.height = _header.height,
this.timestamp = _header.timestamp,
this.previousHash = _header.previousHash,
this.hash = Block.createBlockHash(_header,_data),
this.merkleRoot = Block.getMerkleRoot(_header,merkleroot),
this.data =_data
}
static getMerkleRoot(_data){
const merkleTree = merkle('sha256').sync(data)
const merkleRoot = merkleTree.root()
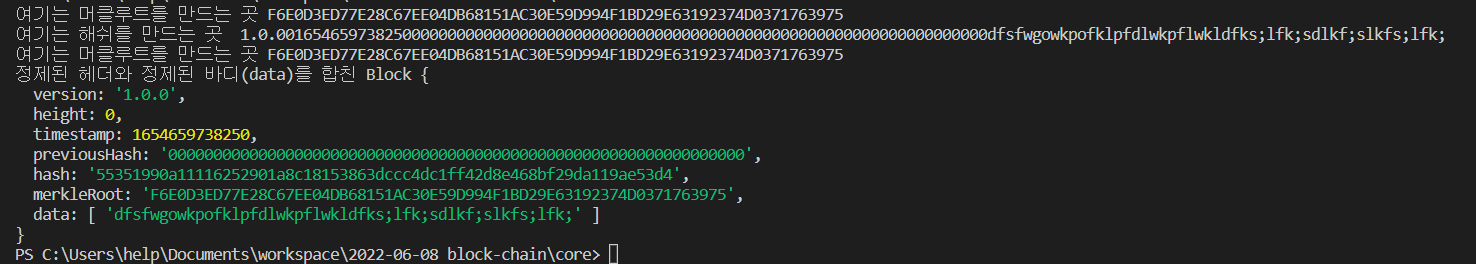
console.log('여기는 머클루트를 만드는 곳',merkleRoot);
// _merkleroot : 1.0.00165465852154000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
return merkleRoot;
}
static createBlockHash(_header,_merkleroot){
//todo : 1. header에 있는 값을 string으로 연결
const values = Object.values(_header)
const data = values.join('') + _merkleroot
console.log('여기는 해쉬를 만드는 곳 ',data);
return SHA256(data).toString()
}
}
// previousHash
// block 연결하는 애가 chain 배워
// blcok 에서 첫번째 블록은 제네시스블록이라고 부름
//new 라는 키워드를 사용해서 class문법을 사용했을 때 나오는 결과물의 객체를 = 인스턴스
const header = new BlockHeader(0)
const data = [ 'dfsfwgowkpofklpfdlwkpflwkldfks;lfk;sdlkf;slkfs;lfk;' ]
const block = new Block(header,data)
console.log('정제된 헤더와 정제된 바디(data)를 합친',block);
// console.log(header.getVersion());
// haeder.getVersion() //static 안붙음
// BlockHeader.getVersion() //static 붙음
// const block = new Block()
// console.log(block);
// hash,merkleroot,genesis block
결과값